Deciding to get breast surgery can be a big decision to make.
After all, there are always risks involved with any type of surgery so it is important to know what you’re getting yourself into.
With surgeries such as breast enlargement, it will involve placing implants into your breasts.
You might be asking questions such as ‘but where does the implant go exactly?’.
Breast implants can be placed using different techniques which allow them to sit in different positions in the breast.
In this post, we will cover the different techniques when it comes to implant placement.
This will allow you to understand the options you have available, should you wish to have breast implants.
How are Breast Implants inserted?
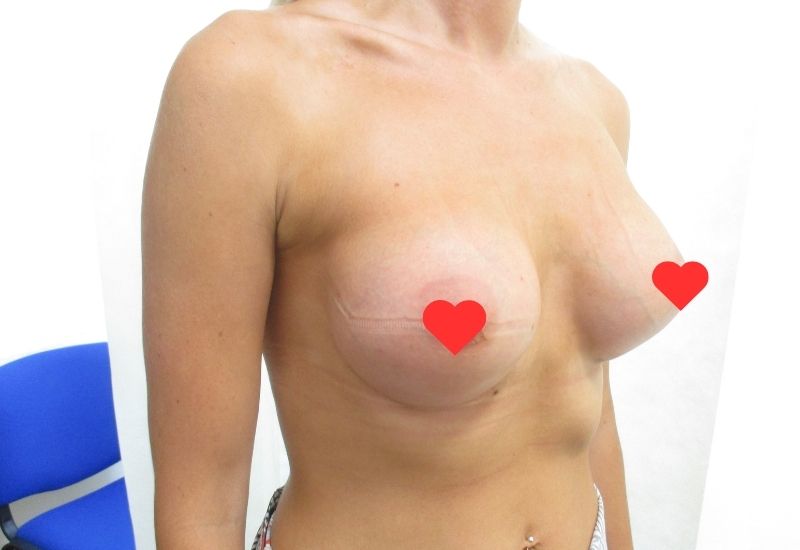
The process of how implants are inserted can vary depending on factors like the type of implant, placement location, and the surgical technique used by the plastic surgeon.
Surgery begins with the administration of anaesthesia to ensure the patient’s comfort and pain relief during the procedure.
The two common options are general anaesthesia (where the patient is unconscious) and local anaesthesia with sedation.
An incision is then made in a predetermined location. The choice of incision site can vary and is often based on patient preference, the type of implant, and the surgeon’s recommendation.
After the incision, the surgeon creates a pocket where the breast implant will be placed. There are three primary locations for the pocket:
- Subglandular (breast implants over the muscle).
- Submuscular (under the muscle implants).
- Dual Plane (Partially under the chest muscle).
For silicone implants, they are pre-filled before insertion, while saline implants are filled with sterile saline solution after placement.
Implants are then carefully adjusted to achieve the desired shape and symmetry. Afterwards, a surgeon assesses the results to ensure they meet the patient’s goals.
Breast implant placement techniques
Now let’s look at the breast implant techniques that are available:
Subglandular Placement

Subglandular implant placement, also known as “over the muscle” placement, is a breast augmentation technique in which breast implants are positioned between the breast tissue and the chest muscle, known as the pectoralis major muscle.
Subglandular placement is often recommended for individuals who have a sufficient amount of natural breast tissue and good skin elasticity.
Advantages
- Quicker recovery – Subglandular placement typically involves a faster and less painful recovery compared to submuscular placement, as the chest muscle is not disturbed during the surgery.
- Natural shape – This may result in a more natural-looking breast shape, especially if you have sufficient natural breast tissue.
- Less complicated surgery – Does not involve dissecting the chest muscle which also leads to less postoperative discomfort.
- Easier revision surgery- If future revision surgeries are needed, such as implant replacement, sub-glandular implants may be easier to access.
Disadvantages
- Potentially more rippling – This is because very little separates the implant from the skin’s surface so rippling has more change occurring.
- Capsular contracture – If capsular contracture occurs when an implant is inserted then it can cause the implant to feel firm or hard. Capsular contracture is a condition where scar tissue around the implant tightens, distorts the breast shape, and may cause discomfort.
The type of implant inserted can play a role in capsular contracture also. A 2006 study found that textured implants reduce the incidence of early capsular contracture in sub-glandular breast augmentation.
- Limitations for some patients – Subglandular placement may not be suitable if you have very little natural breast tissue, as there may not be enough coverage to conceal the implant.
- Bottoming out can occur – This happens when your breast implant descends too low on the chest making the nipple too high on the breast mound.
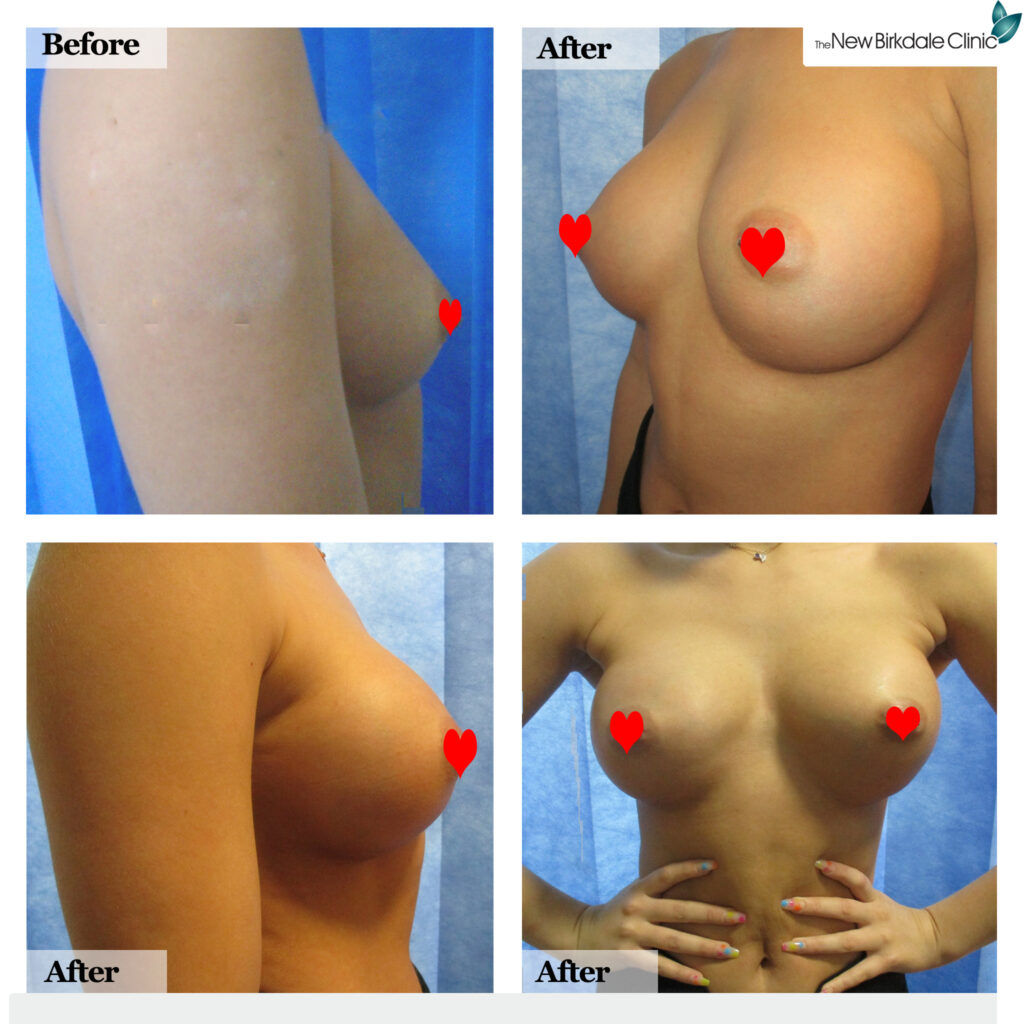
Submuscular placement
Submuscular implant placement, also known as “under the muscle” placement, is a breast augmentation technique in which breast implants are positioned beneath the pectoralis major muscle.
It may also not be suitable for individuals with a significant amount of natural breast tissue, as the muscle may not be necessary to cover the implant adequately.
Advantages
- Natural appearance – Submuscular placement typically provides a more natural appearance and movement of the breasts. The chest muscle helps to conceal the upper portion of the implant, reducing the risk of visible implant edges.
- Lower risk of capsular contracture – This placement option is associated with a reduced risk of capsular contracture.
- Reduced risk of rippling – Submuscular placement can help minimise the risk of visible rippling or palpability, especially in patients with thin breast tissue.
- Mammography – It can be easier to perform and interpret mammograms with implants placed under the muscle.
- Implant protection – The muscle provides additional protection for the implant, which can lead to a longer-lasting result.
- Less sagging – Lower muscle holds up the breast implant to prevent it from sagging.
Disadvantages
- Extended recovery period – Submuscular placement often involves a longer and potentially more uncomfortable recovery period compared to sub-glandular placement. The chest muscle dissection can lead to increased postoperative discomfort.
- Muscle flexing – If you flex your chest muscles this can affect the appearance of the breast and make them look unnatural. This could be more of a concern with athletes and bodybuilders.
- Prolonged drop and fluff – The dropping and fluffing of the implant can take longer to occur.
- Restrictions on implant size – The pectoralis muscle may limit the size and projection of the implant that can be accommodated. Extremely large implants may not be suitable for submuscular placement. Studies have also shown that larger implants when placed using the submuscular placement method are a significant risk factor for implant rupture.
- Limited movement – For some patients, the implants positioned beneath the muscle may limit the natural movement of the breast, potentially impacting the appearance when lying on your back or during physical activities.
Dual-plane placement
Dual-plane implant placement is a technique that combines elements of both sub-glandular and submuscular placements.
It involves creating a breast implant pocket that lets the implant be positioned partly under the muscle and partly beneath the breast tissue.
The upper part of the implant will be under the muscle while the lower part is placed under the tissue.
Dual-plane implant placement is often recommended for individuals who have some breast tissue but may benefit from the additional coverage provided by the muscle for the upper part of the implant.
Advantages
- Capsular contracture – Still a lower risk of capsular contracture than if the implant was placed under the breast tissue
- Natural appearance – Dual-plane placement can offer a more natural appearance. This is achieved by providing the upper portion of the implant with the coverage and support of the chest muscle. This particular study showed that a dual-plane technique was used on a patient and helped reduce the appearance of rippling and gave a more natural-looking breast.
- Less muscle distortion – Dual-plane placement typically reduces the risk of muscle distortion during exercise.
- Mammography – If you need a mammogram then a dual-plane implant placement will give easier access to images and reading.
Disadvantages
- Rippling – If rippling does occur it will likely be on the lower section of the implant which is underneath the tissue.
- Moderate surgical complexity – Dual-plane placement requires a higher level of surgical skill and precision due to its dual-layer approach, which can result in a slightly longer operative time.
- Recovery similar to submuscular placement – While the recovery may not be as extensive as full submuscular placement, it is still associated with a longer and potentially more uncomfortable recovery compared to sub-glandular placement.
- Potential for implant shifting – There is a slight risk of the implant shifting from its initial position due to muscle contractions or activities, which might require revision surgery.
Breast Implant Techniques with The New Birkdale Clinic
As you can see there are breast implant techniques that are suited to your particular situation.
You may not be totally sure of which technique you should go with.
That is why it is always advised to have a professional to speak to about your options.
That is where New Birkdale Clinic comes in.
Thanks to our years of rich industry experience in cosmetic surgery, we have professionals on site who can talk you through which implant techniques are best suited to you.
If you would like to know more about any of these breast implant techniques and get started with your breast enlargement surgery journey then please contact us today.
